Sore Throat Types: An Overview
Sore throat is one of the most common problems seen in any family physician’s or pediatrician’s office. The vast majority of the time it is one of a few diseases that are either self-limiting or easily treated. Let’s first discuss when you can manage the problem yourself without seeing the doctor, and then list the common types of sore throat and describe their signs, symptoms and management.
Sore throats that are the primary symptom, meaning there is not a lot of nasal and head congestion, cough, and sneezing associated with them are more likely to be strep throat than when these other symptoms are present. Fever over 101.4 degrees Fahrenheit, or 38 degrees centigrade, are more likely to warrant evaluation. Inability to swallow, especially to swallow your own saliva is a warning sign of more serious problems and needs evaluation. Recent close exposure to strep throat, younger age, and sudden onset also make strep throat more likely.
Now let’s list the common causes of sore throat and discuss their symptoms and management:
- Viral Pharyngitis: This is the sore throat that is caused by a variety of viruses that are also associated with the common cold. They tend to be associated with other upper respiratory symptoms like congestion, cough, sneezing and sometimes vomiting or diarrhea. They usually don’t have high fever, and don’t require or benefit from a physician evaluation.
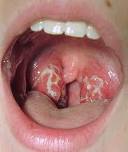 Strep throat: This is the sore throat that patients most often suspect when they go to the doctor’s office. It usually has moderate to severe sore throat as the primary symptom, and often has a fever, aches, chills and headache. Physical signs may include a very red pharynx with petechiae on the soft palate, a shaggy white or yellowish exudate on the tonsils, and have painful enlarged lymph nodes in the anterior neck area. Patients worry about whether strep throat contagiousness, but it’s less contagious than most other respiratory illnesses, though it can be spread by coughing or sharing eating utensils. Children are much more likely to have strep as a cause of sore throat than adults. Strep throat treated in the first day or two of symptoms may resolve faster with antibiotic treatment, and treatments reduces the period of contagiousness and lessens the chances of recurrence.
Strep throat: This is the sore throat that patients most often suspect when they go to the doctor’s office. It usually has moderate to severe sore throat as the primary symptom, and often has a fever, aches, chills and headache. Physical signs may include a very red pharynx with petechiae on the soft palate, a shaggy white or yellowish exudate on the tonsils, and have painful enlarged lymph nodes in the anterior neck area. Patients worry about whether strep throat contagiousness, but it’s less contagious than most other respiratory illnesses, though it can be spread by coughing or sharing eating utensils. Children are much more likely to have strep as a cause of sore throat than adults. Strep throat treated in the first day or two of symptoms may resolve faster with antibiotic treatment, and treatments reduces the period of contagiousness and lessens the chances of recurrence.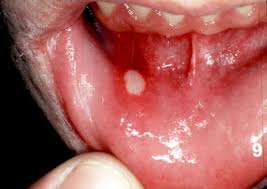 Cancre sores: These are also called apthous ulcers, and are white sores in the mouth that are self-limited and not helped by treatment. They can be very painful when on the back of the throat.
Cancre sores: These are also called apthous ulcers, and are white sores in the mouth that are self-limited and not helped by treatment. They can be very painful when on the back of the throat.- Infectious mono: This is a less common cause of sore throat. It tends to come on gradually, and linger. Large lymph nodes in the front and back of the neck are common, and the tonsils can be very large and covered with a dense white or
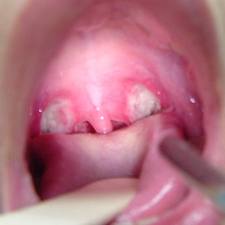 gray exudate. If suspected doctors can diagnose this with blood tests, but no treatments are effective except for symptom reduction. How contagious Is mono is a common question. It’s called the kissing disease, and is spread by saliva exchange primarily.
gray exudate. If suspected doctors can diagnose this with blood tests, but no treatments are effective except for symptom reduction. How contagious Is mono is a common question. It’s called the kissing disease, and is spread by saliva exchange primarily. - Post nasal drainage: This is caused by allergies, a cold, sinus infection or other causes of runny nose where the mucus drains down the back of the throat and causes sore throat. Most causes resolve on their own or with treatment of the underlying problem.
- Rare causes: diphtheria, gonorrhea of the throat, trauma, thrush, throat cancer, lymphoma, and other rare causes are really beyond the scope of this post.
Hopefully this has been useful and of interest.